Configure rolling backups with rsnapshot
Oct 22, 2021 by Thibault Debatty | 3125 views
https://cylab.be/blog/183/configure-rolling-backups-with-rsnapshot
In this blog post we show how to use rsnapshot to configure nice and easy rolling backups.
How it works
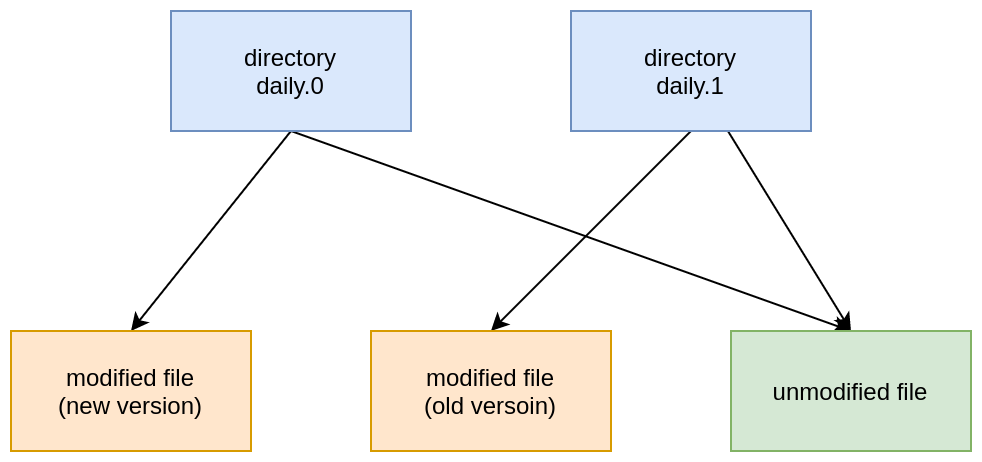
rsnapshot is actually a script that relies on rsync to perform the backups. This is actually extremely clever, as rsync uses hard links and only creates a copy of files that have been modified since the last backup.
This has 2 advantages:
- each backup is a simple replica of the whole directory structure;
- you don’t need any special tool to browse or restore the backup, or a single file from the backup;
- backups are very light and fast, as only new or modified files are copied.
This is actually pretty similar to the way git handles commits internally…
Installation
As easy as
sudo apt install rsnapshot
Configuration
The configuration file is located at /etc/rsnapshot.conf. The most important directives are:
snapshot_root : where rsnapshot must save backups. This should be an external device or a directory on a network drive…
snapshot_root /mnt/nfs/rsnapshot/
no_create_root : rsnapshot should abort if the root directory is absent (i.e. if the external drive is removed or the network drive unavailable):
no_create_root 1
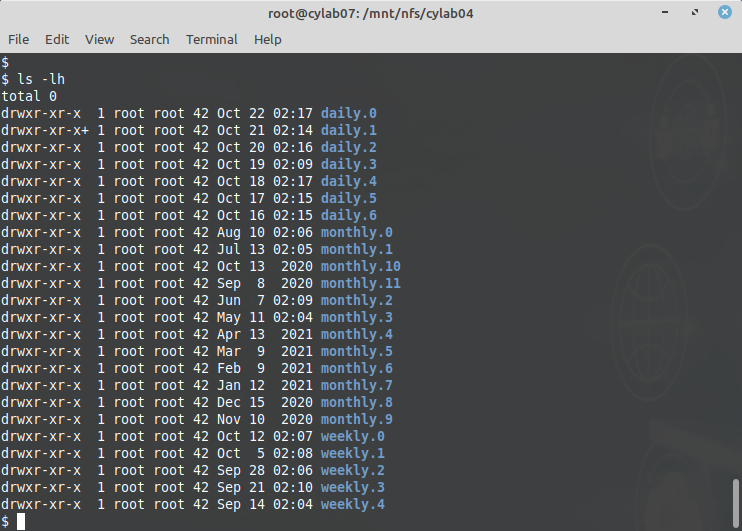
retain : allows to define different “kinds” of backups and the number of copies to keep for each. I like to keep 7 daily backups, 5 weekly backups and 12 monthly backups. So my configuration looks like:
retain daily 7
retain weekly 5
retain monthly 12
backup : indicates which directories must be saved, and where inside the snapshot_root, for example:
backup /var/www www/
Good to know:
- there can be multiple
backupdirectives in your configuration… - configuration directives and options must always be separated by a single tab.
Finally, you can test your configuration with
sudo rsnapshot configtest
Crontab
Now, we must configure crontab such that daily backups take place every day, weekly backups every week, and montly backup every month:
sudo nano /etc/crontab
## rsnapshot backups
# m h dom mon dow user cmd
55 1 * * * root rsnapshot daily
55 2 * * 1 root rsnapshot weekly
55 3 1 * * root rsnapshot monthly
After a few days (and months), your snapshot_root directory will be filled with the appropriate backups directories…
This blog post is licensed under
CC BY-SA 4.0