Out-of-band server management : DELL iDRAC
Mar 10, 2025 by Thibault Debatty | 3169 views
https://cylab.be/blog/393/out-of-band-server-management-dell-idrac
Out-of-band management is a powerful but sometimes overlooked feature of modern servers. In this blog post I’ll showcase some of the features of iDRAC, the out-of-band management system you can find on DELL servers.
Versions and conventions
iDRAC, which stands for Integrated Dell Remote Access Controller, is the out-of-band management system integrated in Dell servers. So it is the DELL equivalent of HP Integrated Lights-Out (iLO).
Like iLO, iDRAC is a small embedded system, inside the server chassis, that allows to reboot and manage the server hardware from a web interface, even if the actual server is down or crashed. The current versions of iDRAC are actually running Linux and Busybox [1]
iDRAC comes in 4 versions: Basic, Express, Enterprise and Datacenter. The details of each version can be found in [4], but here is a quick summary:
- Basic offers all the main functionalities, including remote management, monitoring etc.
- Express adds (a.o.) GPU Inventory and Monitoring, SFP+ Optical I/O Inventory and Monitoring, PKI authentication, advanced power management and crash screen capture.
- Enterprise adds Zero Touch auto configuration, Active Directory and LDAP integration, SSO, 2FA and crash screen video.
- Datacenter includes additional security mechanisms, storage drives SMART logs management and airflow management.
The version you get depends on the server you buy:
- iDRAC Basic comes standard on 100-500 series rack/tower servers.
- iDRAC Express is the standard version on rack/tower servers 600 series and higher.
- iDRAC Enterprise and Datacenter are an option for all serves.
DELL servers naming convention
In the example server DELL R6515:
- R stands for rack, could also be T for tower or M for modular (traditional blade servers)
- 6 is the series (series 1 to 3 have a single-socket, series 4 to 7 are dual-socket server, series 8 has 2 or 4 sockets and series 9 has 4 sockets)
- 5 is the generation (15th gen)
- the last digit (5 in the example) indicate the CPU manufacturer (0 for Intel, 5 for AMD)
- if the server name has 4 digits, the penultimate digit (1 in the example) indicates the number of CPU’s.
Initial configuration
For the initial configuration, connect the iDRAC dedicated port to the network. You should use a dedicated management network for this…
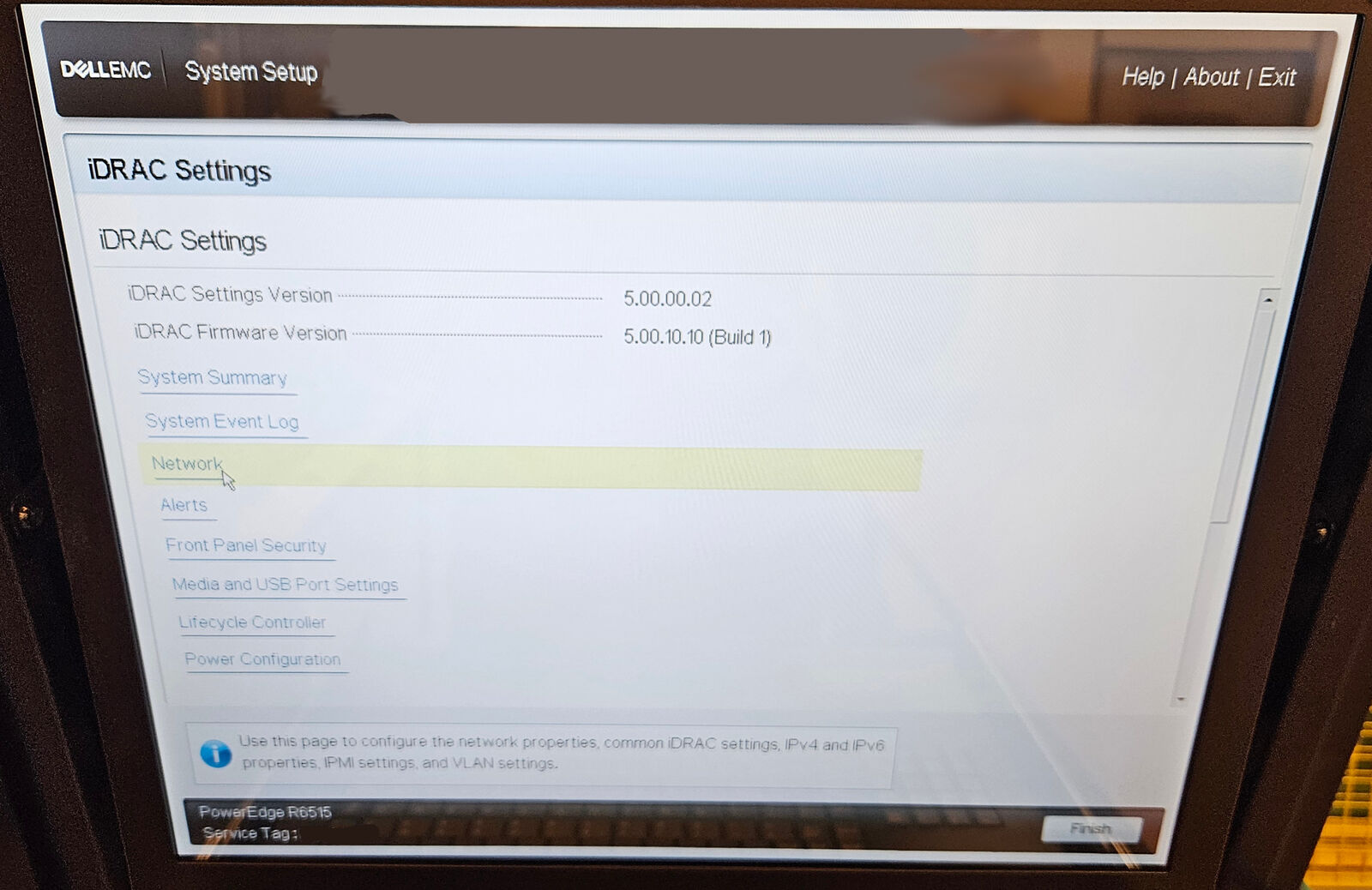
When the server boots, hit F2 to enter iDRAC settings. Here you should configure the network parameters to assign a static IP address, and the login credentials.
Once done, you can access the iDRAC web interface at https://<ip.of.idrac>, even if the server id down.
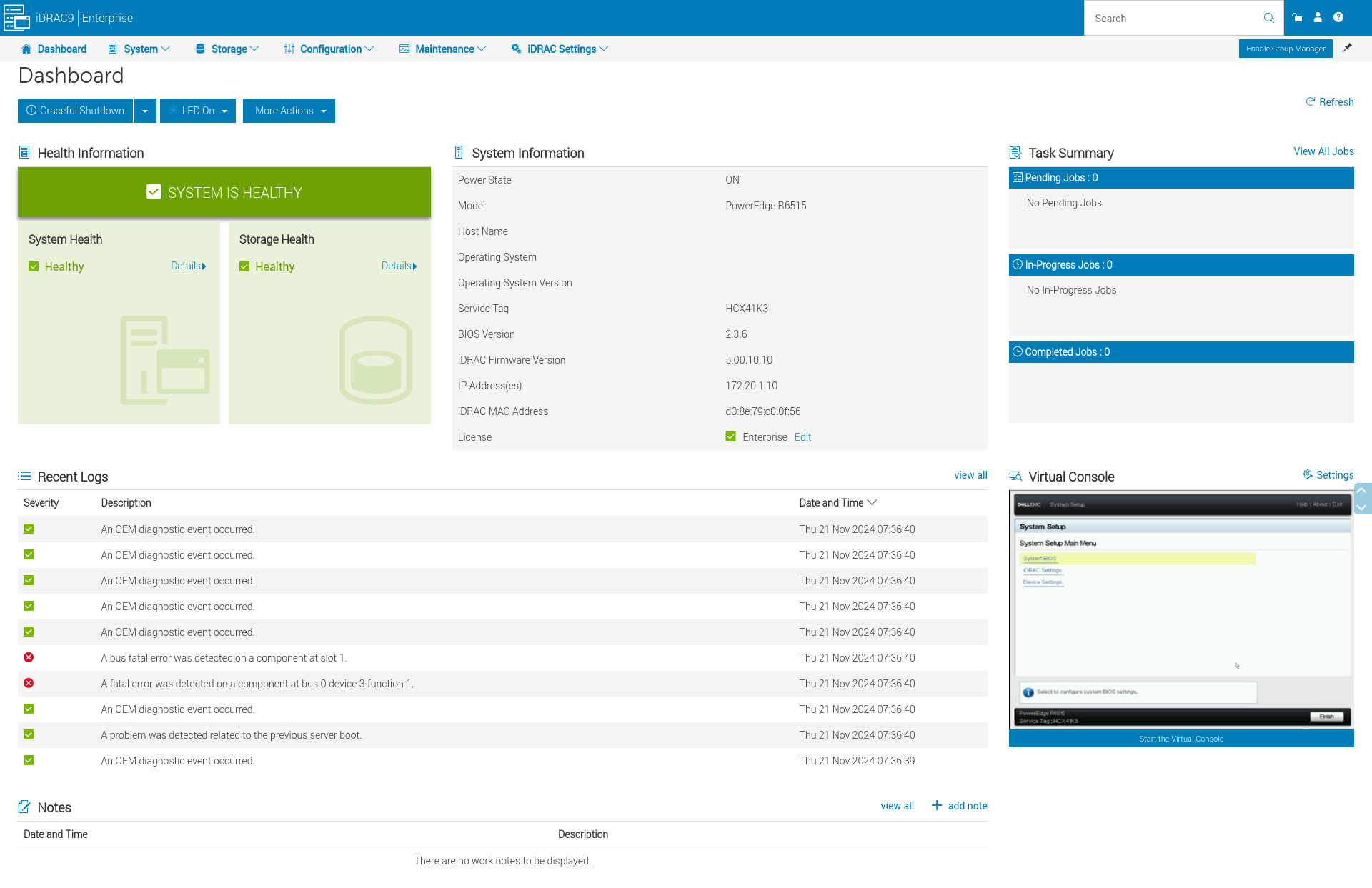
iDRAC web interface
The dashboard provides you with a nice overview of the server status, including storage status. From here you can also reboot a crashed server or start a server that’s down.
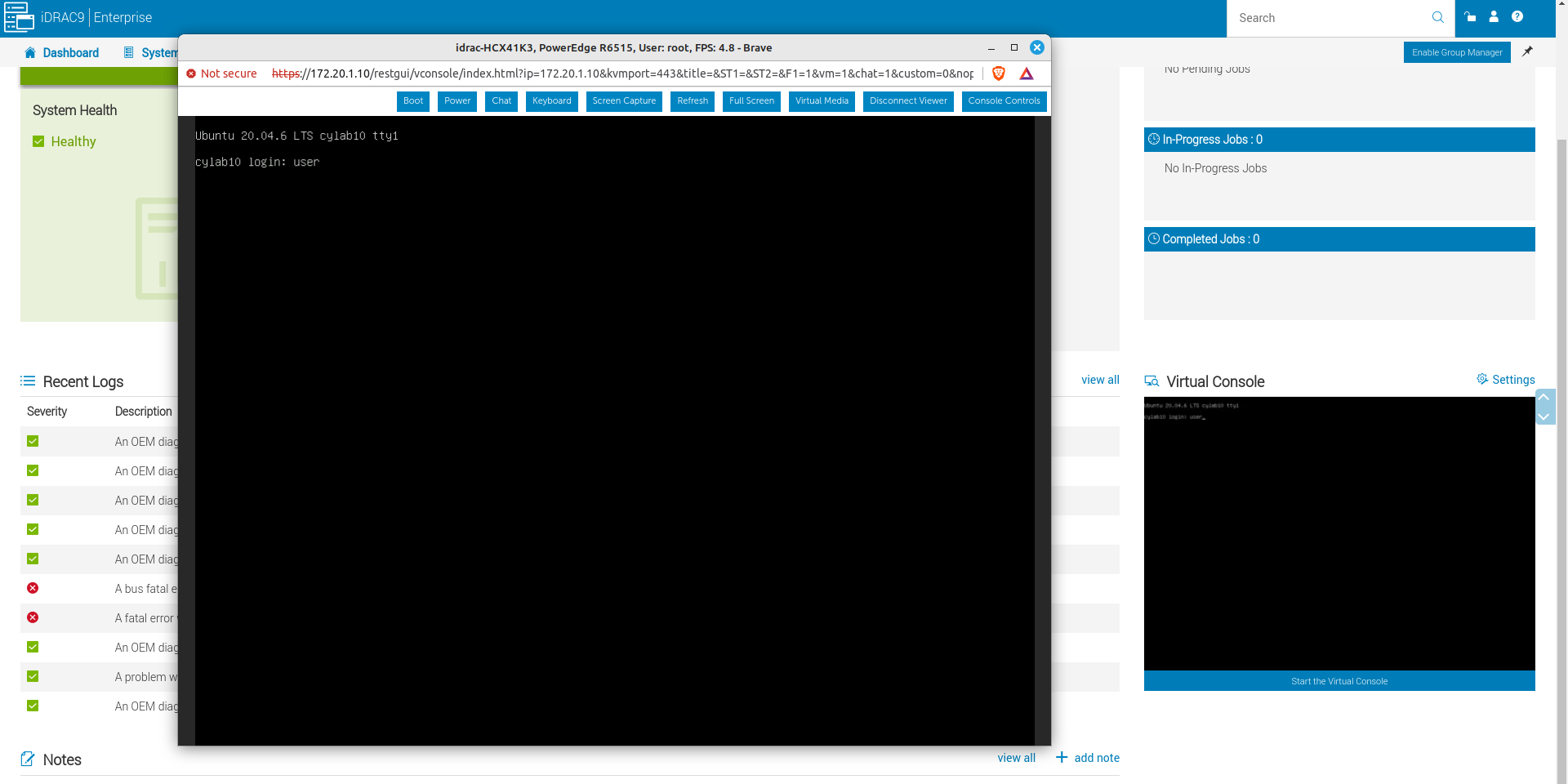
The dashboard also give access to the remote console.
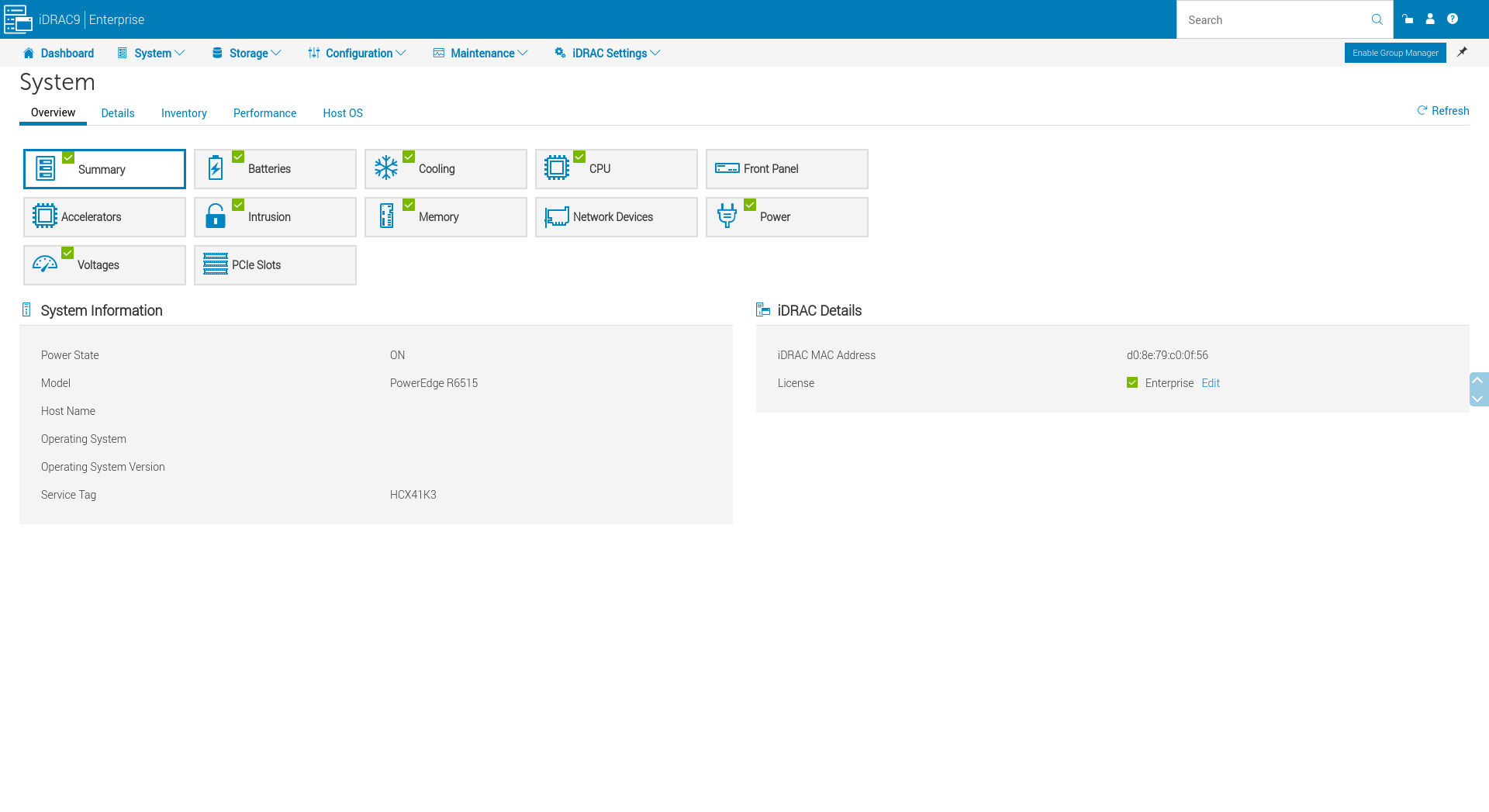
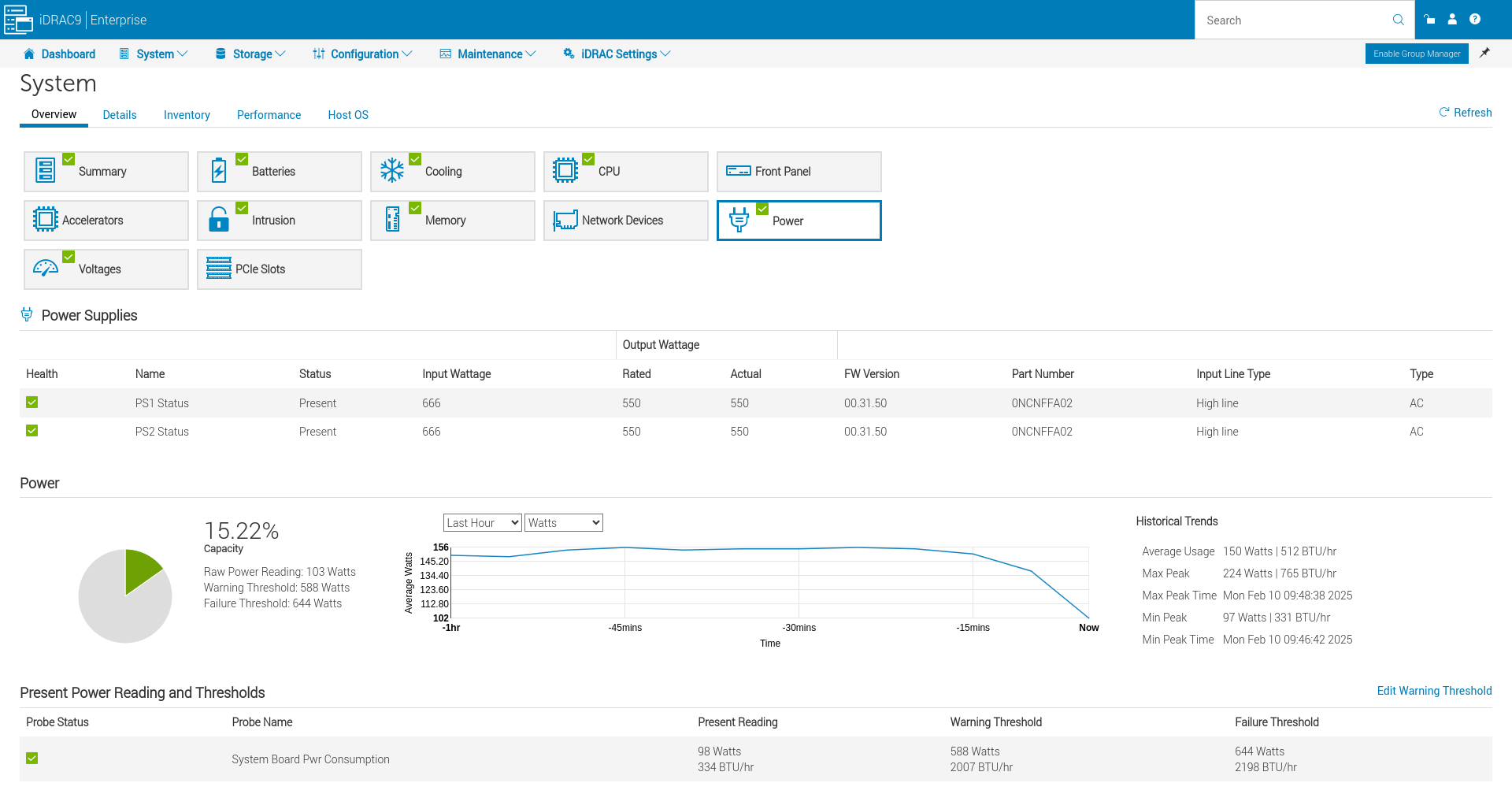
The System tab provides detailed information on the system, including RAID controller status and power supply status.
The storage page allows to monitor and configure the RAID controller, for example to create storage volumes.
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dell_DRAC#Implementation
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dell_DRAC
- https://www.renewtech.com/blog/understanding-the-dell-poweredge-server-naming.html
- https://www.delltechnologies.com/asset/en-my/products/servers/industry-market/openmanage-portfolio-software-licensing-guide.pdf
This blog post is licensed under
CC BY-SA 4.0