Using OpenRouter for single API key access to all your LLM models
Aug 7, 2025 by Cylab Researcher | 8728 views
https://cylab.be/blog/432/using-openrouter-for-single-api-key-access-to-all-your-llm-models
When developing LLM-based applications, it can be tedious or undesired to create and manage API keys with multiple LLM providers. OpenRouter does away with this, by offering a one-stop-shop for contacting and provisioning all of your LLM models; with a single API key.
What is OpenRouter and how to get started
With connections to more than 400 LLMs, some of them free, OpenRouter (https://openrouter.ai/) is a platform that dispatches calls to various models and even distributes those calls between models or model providers in case of errors or unreasonable response times. In what follows, we explain how to quickly start using their service, along with some advantages.
First, you sign up for an account using your e-mail address, Google account or GitHub profile. Next you create a first API key. As already mentioned, this will be the only key you need to call as many LLMs as needed later on. 
Next, you provision your account with some credits. Another advantage here is the possibility to use “one-time payment methods”, meaning that no credit card is required and accidental overspending is therefore not a risk. 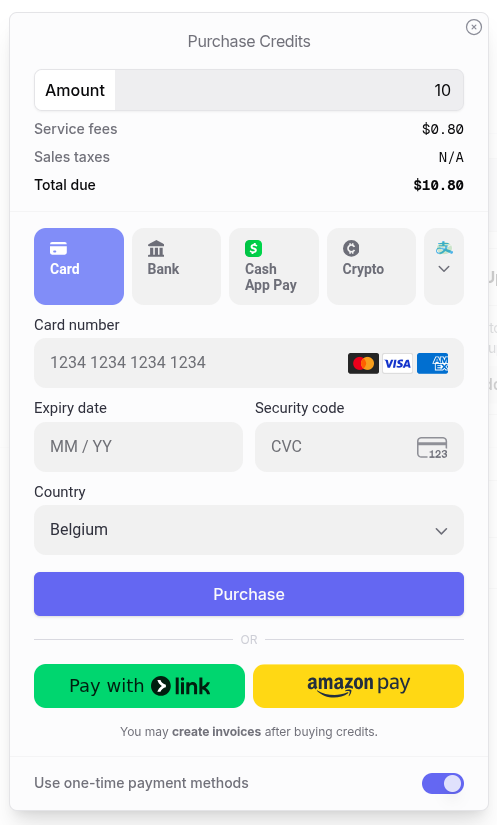
You are now ready to test multiple LLMs from within your code, which we demonstrate in Python below.
Using the OpenAI API
The OpenAI API is well integrated, with some exceptions addressed later. So, for instance, if you have some code lying around that was designed to run GPT models, you can re-use it by simply changing the base_url and api_key arguments.
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from openai import OpenAI
import os
# All credentials are assumed to reside in a '.env' file
# at the root of the python project
load_dotenv("PATH_TO_.ENV_FILE")
client = OpenAI(
base_url="https://openrouter.ai/api/v1",
api_key=os.getenv("OPENROUTER_API_KEY"),
)
#Chat completion mode
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="google/gemini-2.0-flash-exp:free",
extra_body={
"models": [
"openrouter/cypher-alpha:free",
"moonshotai/kimi-k2:free",
"deepseek/deepseek-r1:free",
]
},
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a helpful assistant."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is the meaning of life?"
}
]
)
print(completion.choices[0].message.content)
This code will attempt to send the prompt to and collect the response from Gemini 2.0 Flash Exp; the free version. If the rate limit of a free version is reached, or if you run out of credits, this will simply result in an error returned by the OpenRouter API.
A list of models is available at https://openrouter.ai/models, which you can filter on input media, context length, price, supported parameters and other criteria. Calling a different model is as simple as changing the string value for the model argument above.
In extra_body, it is possible to submit up to three alternative models that OpenRouter would then contact in the case of error or lack of timely response by Gemini, in this case. Of course, if the purpose is to compare specific LLMs, removing this alternative list will force your selected model to be contacted, successfully or not.
Prompt execution by Providers and activity tracking
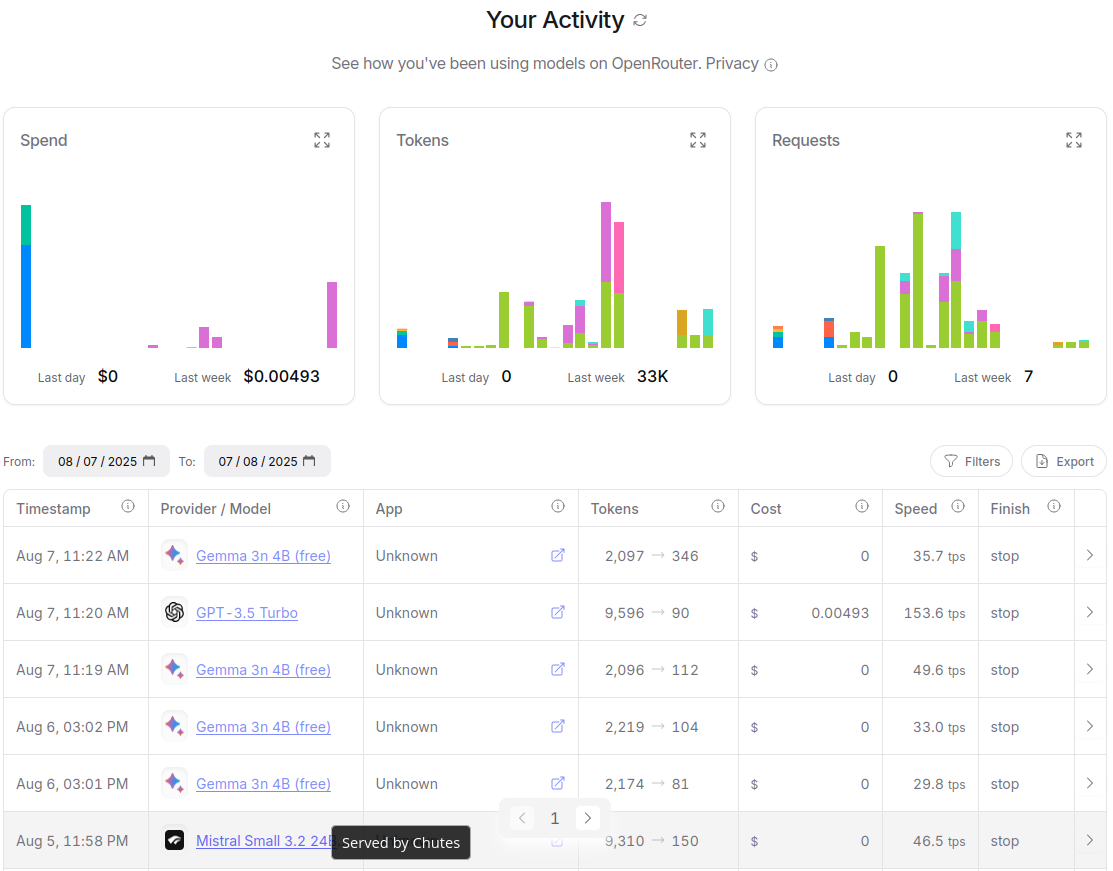
The actual execution of the LLM does not happen on OpenRouter infrastructure but on that of the Providers. These are not necessarily the publishers of the LLM in question, such as OpenAI or Google Gemini. For instance in the screenshot below, the bottom LLM call was that of a Mistral model run by Chutes, which is an independent cloud infrastructure provider (see following screenshot).
This provider happens to also run instances of models from DeepSeek, OpenAI and many more; see https://openrouter.ai/provider/chutes.
The Activity page above is useful to keep track of your LLM costs, but also to confirm which LLM was used; especially if the optional list of alternative back-up models was provided earlier.
No AsyncOpenAI
It is worth mentioning that OpenRouter does not yet support the AsyncOpenAI API. Therefore, to serve the prompt response asynchronously, you will need to import a library like asyncio and define an asynchronous function as follows; compare with the code above.
# Synchronous OpenAI call in an async handler
def get_openai_response():
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model= model,
messages=[
{"role": "user",
"content": question,
}
],
stream=False,
)
return response
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
raw_answer = await loop.run_in_executor(None, get_openai_response)
answer = raw_answer.choices[0].message.content
[...]
Free models but …
Another point of importance is the fact that the free models are not always consistently available. The author has experienced no particular issue with google/gemma-3n-e4b-it:free nor with deepseek/deepseek-r1-0528:free. However, on several occasions, free models such as qwen/qwen3-coder:free seem to come and go without warning. Another example is the obscure openrouter/cypher-alpha:free that the author used but is, at the time of writing, nowhere to be found anymore… One can assume and hope that paid models are provided more reliably.
As a whole, using OpenRouter is a smooth and rewarding experience, with cost security and as simple an API key management as can be.
This blog post is licensed under
CC BY-SA 4.0


