Getting started with MARk : create a PHP data injector
Nov 19, 2020 by Thibault Debatty | 3121 views
https://cylab.be/blog/105/getting-started-with-mark-create-a-php-data-injector
The Multi-Agent Ranking framework (MARk) aims to provide all the building blocks that are required to build large scale detection and ranking systems. For this blog post we will use docker and docker-compose to run a MARk server, then we will use PHP and composer to inject data in the framework.
Concepts
But first a few key concepts:
- MARK is made to analyze a flow of data that continually enters the system, and produce one or more ranking lists, based on some detection algorithms.
- As the flow to analyze can be extremely fast, MARk uses a micro-batch approach: incoming data is recorded for 10 seconds (can be configured), then MARk will check what detection algorithms should be triggered.
- Trying to analyze all the data with one single complex algorithm makes it very difficult understand why a subject received a higher score than another. It’s even worse if you try to debug the algorithm. Hence in MARk the ranking is based on multiple heuristics or algorithms (agents), that should be as simple as possible. The score produced by the different agents can be combined using different aggregation algorithms to produce the final ranking.
- Detection agents are as simple as possible: they are short-lived functions that will be started and executed by the framework when new data is received.
Start an empty server
The easiest way to start a MARk server is using Docker and docker-compose. So you should first create a file docker-compose.yml with following content:
version: '2.0'
services:
mark-web:
image: cylab/mark-web:1.3.2
container_name: mark-web
environment:
- MARK_HOST=mark-server
- MARK_PORT=8080
ports:
- "8000:80"
depends_on:
- mark
mark:
image: cylab/mark:2.2.1
container_name: mark-server
volumes:
- ./modules:/mark/modules
environment:
- MARK_MONGO_HOST=mark-mongo
ports:
- "8080:8080"
depends_on:
- mongo
mongo:
image: mongo:4.4
container_name: mark-mongo
Then you can start the containers with:
docker-compose up
This will create 3 containers:
- a mongodb container to store data;
- the web interface for MARk;
- the MARk server itself.
After a few seconds MARk will be up and running.
The web interface will be available at http://127.0.0.1:8000 The default credentials are:
- E-Mail:
mark-admin@cylab.be - Password:
change-me!
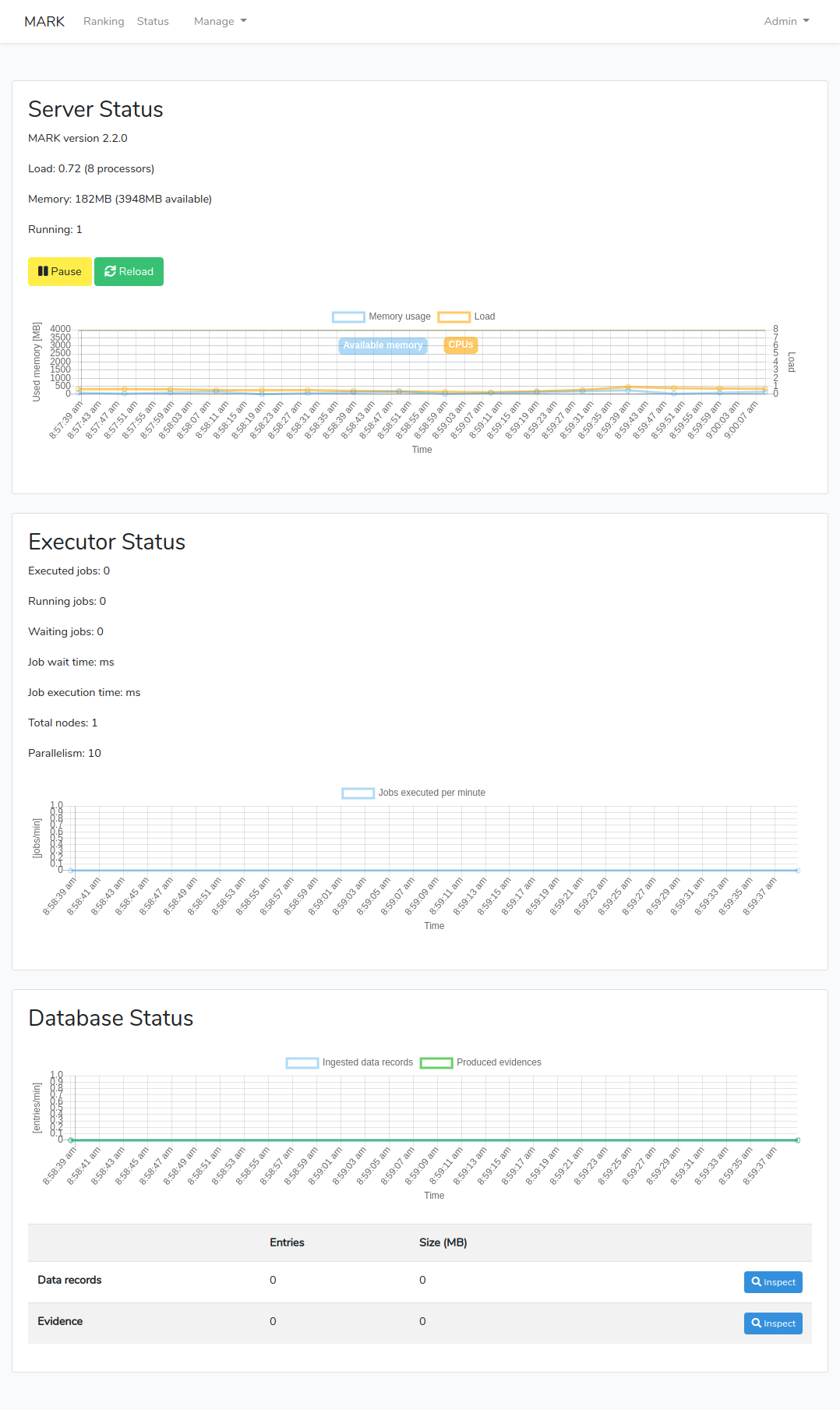
Currently there is not much to see as there is no data entering the system, and no detection algorithm configured. You can browse to the Status page to check that MARk is running smoothly.
Create a PHP data injector
We will now use PHP to inject data into MARk. First, create a new composer project:
composer init
Now you can use composer again to download and install cylab/mark-php-client, the PHP library that allows to easily connect and use the MARk server.
composer require cylab/mark-php-client
Now we can start writing our code. We will first write a small script that checks the status of the server. So this is basically the equivalent of the Status page of the web interface. Let’s call it status.php :
<?php
require_once __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
$client = new CylabMarkClient();
var_dump($client->status());
You can run your script with
php status.php
We can now create a data injector. For this tutorial we have different cats, and we will have to rank them according to some very smart criteria! So let’s create a script called injector.php :
<?php
require __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
$subjects = ["garfield", "snowball", "felix", "hello"];
$server = new CylabMarkClient();
while (true) {
echo "Insert a record ...
";
// select one of the cats at random
$subject = $subjects[array_rand($subjects)];
$record = new CylabMarkRecord();
$record->data = rand();
$record->label = "data";
// time must be expressed in milliseconds!
$record->time = time() * 1000;
$record->subject = ["name" => $subject];
$server->addData($record);
sleep(2);
}
You can now run the injector:
php injector.php
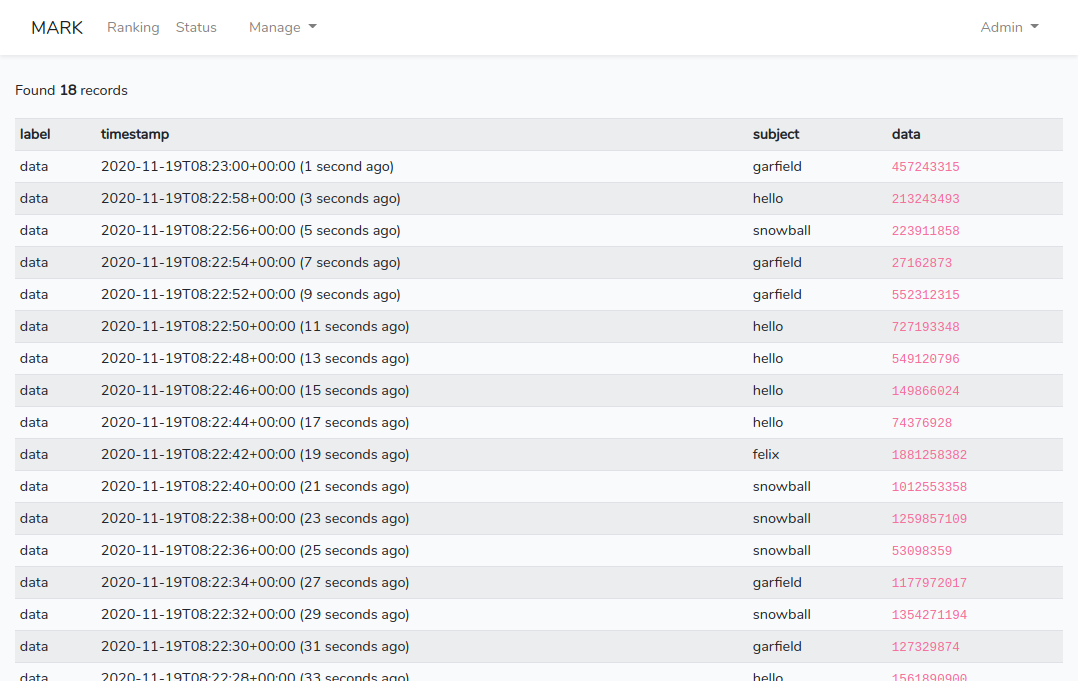
On the web interface, you will see that data is now flowing into the system:
And by clicking on ‘Inspect’ you can even what this data is looking like:
Final words
So now you have a running MARk server, with a PHP injector. In the next tutorials we will see how to use and configure the built-in detection algorithms, then how to create you own algorithms.
This blog post is licensed under
CC BY-SA 4.0